Urinary tract infection: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments

Urinary tract infection & its causes are a common type of infection that can affect some parts of your urinary system. It could be the urethra (urethritis), kidneys (pyelonephritis), or bladder (cystitis). Such infections can have serious implications and thus should be treated immediately.
Women have a greater chance of getting a urinary tract infection (UTI) than men. Not only can it be a source of irritation, but if the bacteria reach the kidneys it can also cause serious health issues. That’s why it is important to keep an eye out for any UTI-related symptoms.
Our bodies have a natural filtration system to rid the body of waste and excess water, creating urine in the process. As a byproduct, urine doesn’t usually contain any bacteria or germs. Usually, urine will flow into the urinary system without any risk of infection. If a urinary tract infection occurs, healthcare providers will focus on treating it with antibiotics. Also, there are steps you can take to reduce the possibility of getting a UTI in the first place.
Table of contents
Who gets causes urinary tract infections?
UTIs affect both genders but occur more often in women due to their shorter urethra which is nearer the anus. The E.coli bacteria that causes the infection is also more common in this area. Older individuals are also more prone to developing cystitis due to weakened immunity and other age-related changes. The risk of incomplete bladder emptying may be attributed to various medical issues, such as an enlarged prostate or a bladder prolapse. In the latter case, the organ falls out of its normal position.
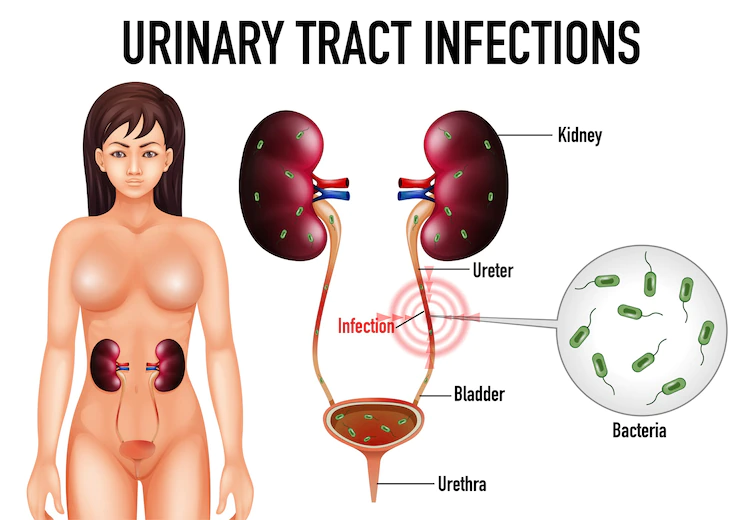
If you are suffering from recurrent UTIs, your doctor can run several tests to check for any underlying health conditions like diabetes or an irregular urinary system that might be causing it. This way, you can get the necessary help and be on your way to recovery. Those who experience regular UTIs may occasionally be supplied with a course of low-dose antibiotics, to help stop the infection from recurring. Medical experts take a cautious approach when it comes to treating UTIs as they can lead to antibiotic resistance and other infections such as C. diff colitis. This practice is only used sparingly due to the risks involved.
Urinary tract infection Causes
A urinary tract infection (UTI) usually happens when bacteria travel through the urethra and enter the bladder, causing an increase in germs in the area. The urinary system has certain defense mechanisms to keep bacteria out. At times, however, there will be breach of these defenses and bacteria can cause an infection in the urinary tract. In such cases, prompt medical attention is necessary to avoid complications.
Urinary tract infections are quite common, especially among women and they can impact the bladder and urethra.
- Bladder infections are typically by the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli). We can see this type of bacteria mainly in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, although there may be other bacteria that can also cause these infections.
- Although sexual activity is a risk factor for bladder infections, it isn’t a requirement. All women bear the risk regardless of their situation since their anatomy exposes them to this issue – with the urethra close to the anus and their urethral opening near their bladder. This causes a higher risk of bacteria from the anus traveling into the urethra and ultimately reaching the bladder
- Urethral infections can arise from the spread of GI bacteria from the anus to the urethra. Their cause may also be by STIs, thus requiring immediate medical attention. Certain sexually transmitted infections, such as herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma can be contracted by women due to the proximity of their urethras close to the vaginal area.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) may not always be obvious; however, when they do appear, they commonly comprise:
- A persistent need to urinate that does not fade away.
- People may experience a stinging or scalding sensation while urinating, which can indicate an underlying medical condition.
- Frequent urination is accompanied by the passing of only small amounts of urine.
- Urine that looks cloudy
- When urinating, keep an eye out for abnormal colors like red, bright pink, or cola-colored. This could be indicative of the presence of blood in your urine and hence needs to be checked by a doctor.
- Strong-smelling urine
- Women can experience pain in their pelvic region, particularly near the pubic bone or in the center of their pelvis.
UTIs are commonly underdiagnosed in older adults, as they may be mistaken for other health issues.
Urinary tract infections Diagnosis
The diagnosis of urinary tract infection can by your doctor through the use of certain tests. These tests involve sampling and testing of your urine.
- Urine tests, known as urinalysis, are to detect infections or diseases. This test is to check for the presence of red & white blood cells and bacteria. The number of these cells found in your sample can point towards an infection or other medical condition.
- Urine cultures are an essential diagnostic tool that helps diagnose the presence of bacteria in the urine. This test can help medical professionals determine the most accurate treatment for a patient.
If antibiotics haven’t reduced your symptoms or the infections keep recurring, your doctor may run certain tests to check for any anomalies in your urinary tract. This will help determine if there is any underlying cause for the infection.
- Ultrasound is a non-invasive test that creates an image of internal organs using sound waves. It can be without any preparation, doesn’t cause pain, and performe over the skin’s surface.
- Cystoscopy is a method to gain a clearer view of the bladder. It involves using special equipment that contains a lens and light source, inserted into the urethra to look inside the bladder.
- CT scans can provide a much more precise look at the body than traditional X-rays. They achieve this by making cross-sections of the body, similar to the idea of slicing it up into different pieces.
Urinary tract infections Treatment
One of the most effective treatments for urinary tract infections is antibiotics as they can effectively fight bacteria and eliminate the infection. Make sure you take the prescribed dosage to get rid of it. To treat Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs), antibiotics are prescribed. Your doctor will decide which is the most suitable drug for your particular infection. Some of the most popular antibiotics used include:
- Nitrofurantoin.
- Sulfonamides (sulfa drugs).
- Amoxicillin.
- Cephalosporins.
- Doxycycline.
You must adhere to your healthcare specialist’s guidelines for taking the medicine. Even if your symptoms diminish and you start to feel better, do not stop taking the antibiotic medication. If the infection is not cured appropriately using a full course of antibiotics, there’s a chance it will come back.

If you’re prone to UTIs, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics for you to take during the early stages of infection. This medication can help reduce the symptoms and prevent further recurrences. If you have a history of recurrent UTIs, your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option with you, which may include taking antibiotics on a daily, alternate day, or post-sexual intercourse basis. This will help reduce the chance of infection.
Complications
Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics for a urinary tract infection is the key to avoiding more serious health complications. If you dont take care of it on time or discontinue the medication is before completion, a kidney infection can be one of the results.
Prevention
UTIs can be avoided by taking certain precautionary measures. These steps could potentially reduce the risk of UTIs:
- To stay healthy, it is important to drink plenty of fluids, particularly water. This helps reduce the concentration of your urine, which in turn leads to more frequent urination. This flushes out any harmful bacteria that might be present in your urinary tract and prevent infections from occurring.
- Cranberry juice may be beneficial in preventing UTIs. Although no studies have officially proven this yet, drinking cranberry juice is not detrimental and might be worth a try.
- Always remember to wipe from front to back after urinating and defecating. This helps stop the transmission of bacteria from the rectum to the vulva, vagina, and urethra. It’s an effective way to prevent infection.
- To safeguard your health, it’s best to avoid any product that can create irritation in the genital area. This includes deodorant sprays, douches, and powders. Urethral irritation can be caused by these products and should therefore be avoided.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) usually have a quick response to treatments. You may feel discomfort before you start the necessary medication by your healthcare specialist, but as soon as the identify the bacteria and the proper antibiotic, you should experience an improvement in symptoms in no time. If you experience any of the symptoms, or if your other symptoms are still present after treatment, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Products That We Suggest for you
Prostacet- Support Prostate Health
The Prostacet Formula delivers key ingredients to nutritionally support a healthy prostate. Prostacet is an outstanding formula that supports prostate health with Serenoa repens which works to nourish this vital organ.
To know more and purchase, Click Here
ProstaStream – Prostate Health Supplement
ProstaStream is an all-natural prostate health dietary supplement for men. ProstaStream’s solution contains all-natural ingredients that are plant, gluten-free, and manufactured in a GMP facility. The solution is have FDA-approval, with no chemicals, or steroids.
To know more and purchase, Click Here








Comment to this Article
Comments that encourage respectful conversation are welcomed at AGP Health n Beauty. Stay on subject, please. Comments that are aggressively promotional of goods or services or that include personal attacks, vulgar language, or other forms of abuse will be deleted. Which remarks break our comment policy will be decided at our discretion. (Anonymous comments are accepted; just leave out your name in the comment box. Although necessary, your email address won't be posted with your comment.)